Integra LifeSciences enhances multicloud capability with OCI, achieves 90% time savings and boosts IT efficiency
October 5, 2021 | 12 minute read
The authors want to thank these individuals at Integra LifeSciences for their contributions: Peter Gawroniak, senior director of infrastructure, Samuel Shonk, director of applications, and Seenu Santhalingam, chief architect.
Integra LifeSciences is a biomedical corporation that’s addressing life-threatening situations with help from Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). Based in New Jersey, United States, Integra is a leading global provider of regenerative and neurosurgical devices and technologies. Integra’s products include tissue technology for wound reconstruction surgery for burn victims, nerve damage, and dura repair, systems for neurosurgery and neuromonitoring, electrosurgery, and advanced monitoring. Their products have become ubiquitous in hospitals and are relied upon by surgeons and patients around the world.
Figure 1: Examples of Integra LifeSciences products
In this technical case study, we dive deeper into Integra’s offerings, their solution on OCI, and results achieved through their partnership with Oracle.
Integra LifeSciences’ goals
Integra has enjoyed unprecedented growth since 1989 through significant acquisitions. As a result, the infrastructure team is constantly pushing the boundaries to support this business. Unfortunately, their initial integration partner had several unsuccessful attempts at migrating workloads to the cloud. The previous vendor had resized the database platform three times during six months, causing a series of service disruptions that affected end-user experience across global teams.
That vendor’s cloud infrastructure issues included incorrect sizing, complexities with pricing, and lack of performance. At the same time, some of Integra’s technologies in colocated data centers were out-of-date and expensive to maintain. Therefore, the corporation had the following goals:
- Successfully migrate all mission-critical E-Business Suite applications and databases to the cloud to take advantage of the elasticity and agility cloud-based infrastructure can provide. With exceptional migration support from the cloud vendor, their implementation partners and in-house IT teams can quickly deploy and integrate new systems that can serve the global end-user base.
- Reliably monitor and manage cloud-based applications at all times so that issues are resolved quickly, and products required by surgeons and healthcare providers aren’t impacted.
- Use high-speed networking to enable comprehensive disaster recovery capabilities and large data transfer for enhanced analytics.
- Provide interoperability between OCI and Microsoft Azure.
Suite of Oracle Cloud services used
OCI’s high-performance platform, including bare metal instances with high I/O NVMe drives and Oracle Exadata Cloud service, was ideal for Integra LifeSciences. Further, Oracle Cloud Lift services offered a compelling option for the company, providing dedicated support from Oracle’s cloud architects. After a successful initial deployment with OCI, Integra decided to move its entire IT back-office to OCI. As outlined later in this article, over 140 systems are being migrated to OCI, across environments for development, quality assurance, production, disaster recovery, and special projects.
The following list includes relevant Oracle cloud services and software:
- Oracle Cloud and Microsoft Azure Interconnect: The Oracle Cloud and Microsoft Azure interconnection allows customers to migrate to the cloud or to build new applications that use the best of OCI and Azure. Customers can move interdependent enterprise applications to the cloud, deploy custom and packaged applications across OCI and Azure, and develop cloud native applications in both cloud environments. Most importantly, customers can migrate on-premises applications to the cloud while preserving application architectures, optimizations, and interoperability.
- Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS): An Oracle packaged application that is trusted by thousands of organizations around the world to run their key business operations like enterprise resource planning (ERP).
- Oracle Exadata Cloud service: Oracle Exadata Cloud service runs on OCI. Dedicated X8M infrastructure is isolated from other users, allowing database teams to improve security, performance, and uptime for customer databases.
- Oracle Active Data Guard: Oracle Active Data Guard provides a comprehensive set of services that create, maintain, manage, and monitor one or more standby databases to enable production Oracle databases to survive disasters and data corruptions.
- Advanced Supply Chain Planning (ASCP): ASCP is a comprehensive, internet-based planning solution that decides when and where supplies, such as inventory, purchase orders and work orders, are deployed within an extended supply chain.
- Oracle Product Lifecycle Management (PLM): Oracle Fusion Cloud software accelerates innovation and new product introductions by efficiently managing items, parts, products, documents, requirements, engineering change orders, and quality workflows across globalized supply chains while seamlessly integrating to computer-aided design (CAD) systems.
- Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC) : Oracle Integration accelerates time-to-live with prebuilt connectivity to any software-as-a-service (SaaS) or on-premises application. The platform includes run-ready process automation templates, real-time business insights, and a visual builder for web and mobile app development.
- Services Oriented Architecture Suite (SOA Suite): The industry’s most complete and unified application integration and SOA solution with simplified cloud, mobile, on-premises, and internet of things (IoT) integration capabilities.
- Oracle Identity and Access Management (IAM): Oracle IAM is a governance solution that provides self-service, compliance, provisioning, and password management services for applications residing on-premises or on the cloud.
- Oracle Governance Risk and Compliance Platform (EGRCM): EGRCM forms a documentary record of a company’s strategy for addressing risk and complying with regulatory requirements. It enables users to define risks to the company’s business, controls to mitigate those risks, and other objects, such as business processes to which risks and controls apply.
- Oracle Cloud Observability and Management Platform: A suite of services for immediate interrogation of assets and allows for machine-learning automation to create actionable insights. It spans all tiers of services, from web to app servers to databases, and drills into underlying compute, storage, and networking layers.
- OCI Logging: DevOps customers can easily review log data, diagnose issues, and use the rules engine to trigger serverless Functions or alerts with OCI Logging service. Built on open standards, OCI Logging is an intuitive, centralized platform for all types of logs, such as audit, infrastructure, database, and applications, which are needed for DevOps and security compliance.
- OCI Compute: Intel and AMD EPYC bare metal servers and virtual machines for database tiers.
- OCI Block Storage: Reliable, high-performance block storage designed to work with a range of virtual machines and bare metal instances. With built-in redundancy, block volumes are persistent and durable beyond the lifespan of a virtual machine and can scale to 1 PB per compute instance.
- OCI Object Storage: OCI Object Storage enables customers to securely store any type of data in its native format. OCI Object Storage is ideal for building modern applications that require scale and flexibility, as it can be used to consolidate multiple data sources for analytics, backup, or archive purposes.
- OCI Resource Manager: Terraform automation as a managed service. The service enables customers to easily automate and manage the deployment of infrastructures for all their workloads, simplifying application lifecycle management.
- OCI FastConnect: FastConnect allows customers to connect directly to their OCI virtual cloud network through dedicated, private, high-bandwidth connections. Based on the amount of data, customers simply choose an appropriate port speed and pay a consistent, low price each month.
- OCI VPN Connect: A simple and secure way to connect corporate networks to OCI.
Integra also uses some non-Oracle applications, including Sabrix tax calculation and reporting and Tidal Software for workload automation.
Integra’s IT systems
Integra’s Oracle E-Business Suite ecosystem is the cornerstone of its billion-dollar revenue stream. This ecosystem contains customer information, configuration data for their cost of goods manufacturing, supply chain tracking, processing, order-to-cash tracking, and other data to facilitate sales and operations.
The E-Business Suite (EBS) ecosystem includes Core E-Business Suite reporting components, Agile, Advanced Supply Chain Planning, and Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC). The second tier includes SOA Suite, Oracle Identity Management (OIM), and some external systems, such as Sabrix Tax and Reporting and Tidal Software. These targets all have an application server tier and a database tier. Active Data Guard handles disaster recovery, replicating data over a high-speed FastConnect network link.
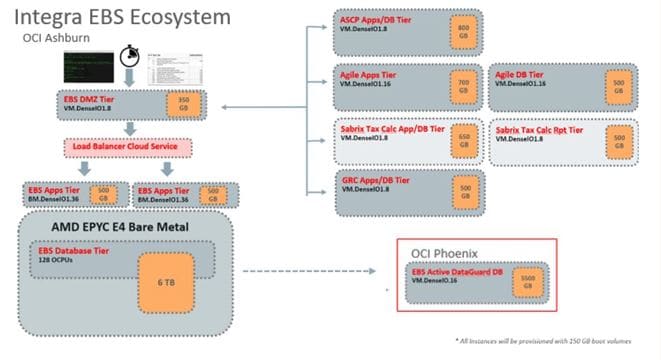
Figure 2: E-Business Suite infrastructure
Integra also has a second system for provisioning infrastructure, which includes Oracle IAM, E-Business Suite, and Active Directory. When users are created in the E-Business Identity store, Oracle IAM also provisions credentials in their corporate Active Directory and enables a corresponding account in Office 365. This automation speeds onboarding time across the platforms and reduces risk of inadvertent misconfigurations.
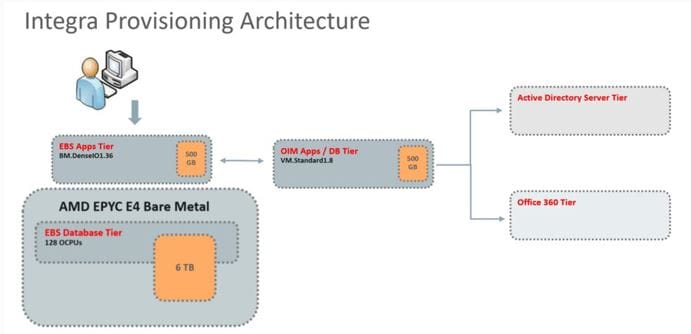
Figure 3: Provisioning infrastructure
The third system deals with external integration and using Oracle SOA Suite, AIA Foundation, PIP, and partner-specific connectors. These systems coordinate between assets stored in the E-Business Suite and enable extended planning and tracking within the Agile subsystem, coordinating activities such as invoice and payments with their trading partners and external SaaS applications such as OTM and GTM.
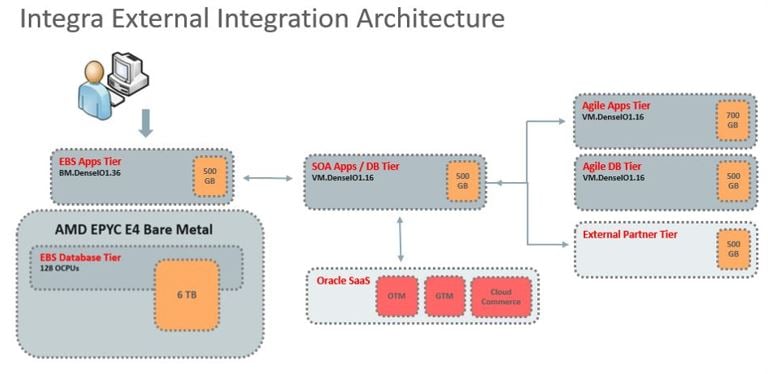
Figure 4: External integration
Migration path to OCI
In May 2019, Integra’s on-premises E-Business Suite compute operations were running at more than 90% utilization. The in-house IT team and partner had to integrate two extra business units over the next six months. If the team maintained the status quo, the deployment footprint would soon be inadequate, especially during month-end, quarter-end, and year-end close processing. So, the engineers needed new strategies to meet the short-term demands and lay the groundwork for an architecture to meet their needs for the future acquisitions.
OCI offers many powerful capabilities to meet these challenges. Central to these offerings is OCI’s cloud regions, which offer dedicated network performance, bare metal instances with high I/O NVMe drives, and Oracle Exadata Cloud service, which enables extreme performance, horizontal scaling, load bursting, and enhanced availability.
Oracle proposed a joint proof-to-pilot (P2P) that demonstrated the advantages of OCI to support Integra’s future state architecture. P2Ps go beyond typical proof of concepts and, as part of this P2P, Oracle worked with the customer to develop success criteria for a subset of use cases and technical stacks. After the conclusion of successful tests and use case evaluations, Integra and Data Intensity took over operations to expand the deployment.
Integra’s systems are complex and highly integrated, and as with any large-scale enterprise, extensive testing must be performed before releasing into production use. The Integra P2P focused on migration of E-Business Suite and its ecosystem components (Agile, ASCP, and GRC) while utilizing Exadata Cloud for the database tier. Integra’s success criteria centered on typical operations, month end report performance, overall functionality, and management of these systems. The following graphic shows the architecture:
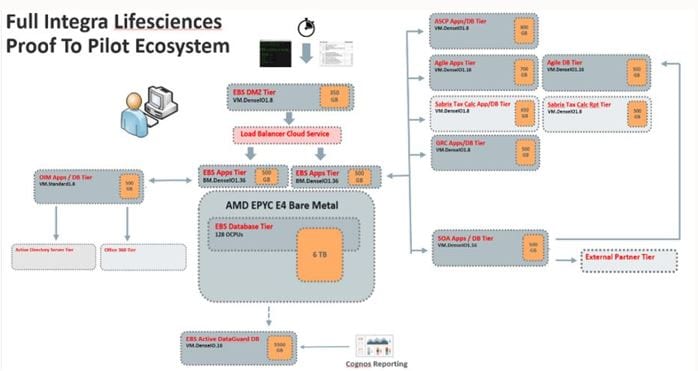
Figure 5: Integra proof-to-pilot: E-Business Suite Ecosystem
Oracle solution architects and Integra worked closely to define all facets of success criteria. First, Integra provided current architectural details for their older hardware. Engineers then ran AWR miner reports that detailed performance loads during the month or quarter close activities. After analysis, Oracle and Integra decided to structure the P2P with a two-node Exadata Cloud deployment for the database tier and two 36-core bare metal instances for the E-Business Suite application and Concurrency Manager tiers.
Integra’s engineers then created automation scripts using Oracle Advanced Testing Suite (OATS) to simulate operations under various virtual user loads. Oracle engineers then built a P2P tenancy and populated it with Integra test data and an Active Directory replica for user credentials. The OATS scripts were moved into the environment for testing to begin.
After the successful conclusion of the P2P, Oracle, Integra, and Integra’s implementation partner, Data Intensity, began to plan a controlled rollout into OCI’s Ashburn region. Cloud services used in the initial deployment included virtual cloud networks (VCNs), subnets, security lists, and gateways. To maintain its stringent FDA certification status, Integra sought a repeatable and error-free build process. The customer and partner used OCI Resource Manager to automate provisioning of OCI resources and OATS to perform functional tests against the deployed servers.
Presently, Integra is deploying several critical environments, from development to quality assurance, production, disaster recovery, and special projects. These environments also needed to be refreshed at regular intervals (many on a nightly basis). Over 140 complex systems are being deployed in OCI. The following image shows a more detailed and unified architectural diagram that outlines the compartments and subnets of Integra’s tenancy.
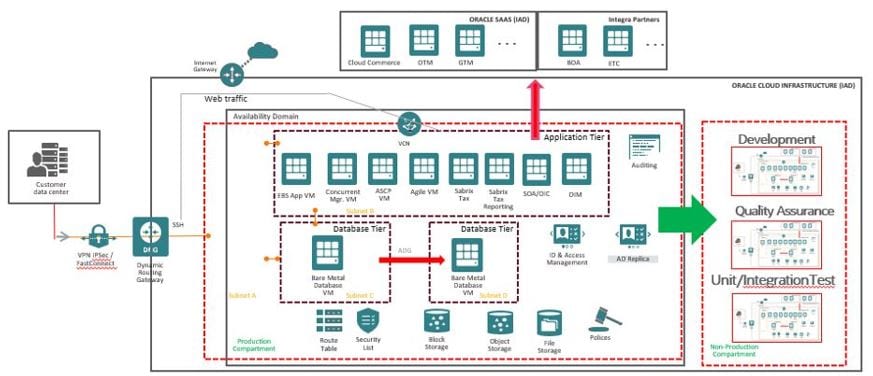
Figure 6: Integra’s production systems architecture
Integra had deployed a data warehouse in Azure but had relied on several manual steps to transfer data from their EBS system on OCI to the data warehouse. Using their traditional processes and standard network connections, Integra’s data refresh times and subsequent analytics reporting windows were inefficient and expensive.
As part of their multicloud strategy, the company leaned on OCI’s interconnection with Microsoft Azure. The Oracle Cloud and Microsoft Azure Interconnect provides a performant multicloud solution that allows customers to migrate to the cloud or to build new applications that use the best of OCI and Azure. Oracle’s FastConnect and Azure’s ExpressRoute networking were connected to provide a dedicated link that bypasses the public internet. Integra deployed the interconnect in few days, enabling cross-cloud data transfers at 10 Gbps and faster processing of analytics reports in Microsoft Azure.
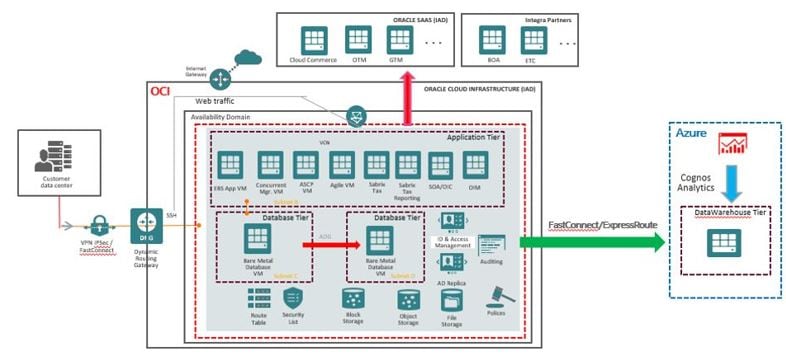
Figure 7: Oracle Cloud and Microsoft Azure Interconnect
Results achieved on OCI
During the P2P evaluation, Exadata Cloud’s performance markedly exceeded Integra’s processing requirements. For example, the daily sales invoice report took about an hour and 45 minutes on the on-premises system. In OCI, with the same number of concurrent users (500) and no changes, the same report ran in 13 minutes: An 87% improvement. Using the in-memory database option increased the time savings to 91%. Numerous other report processing tasks showed similar performance gains.
The company’s IT leaders remarked on more benefits of using OCI, including its multicloud capability. “One of the drivers for OCI was being able to use Active Data Guard to ensure that our data is safe and backed up and improve the resiliency of our platform,” said William Compton, CIO of Integra LifeSciences. “This is a level of business resiliency that we've never experienced before. It's all made possible by OCI and the extensive computing power and elasticity of the platform.”
“We get more proactive performance information from OCI than we've ever gotten from a computer platform in the past,” said Peter Gawroniak, senior director of IT infrastructure and operations. “We can anticipate problems before they happen.”
“Our processing window for our nightly data analytics run was about 8.5 hours,” said Peter Gawroniak, senior director of IT infrastructure and operations. “With the combination of the backbone interconnection between the Azure and OCI platforms and the extensive horsepower on OCI, we moved that window to about 3.5 hours on a nightly basis.”
Next steps
By undertaking a P2P deployment and extending OCI’s functionality to production workloads, Integra LifeSciences has minimized risk while strategically positioning itself for high growth. OCI capabilities and the workloads it supports aligned with interoperability with Microsoft Azure not only brings the necessary performance but visibility throughout Integra’s entire supply chain for better coordination among global teams. Integra’s technology team continues to test and evaluate more Oracle Cloud Infrastructure capabilities, including Oracle Real Application Clusters, Oracle Integration Cloud, and Oracle Digital Assistant.
Use the following resources for more information:
- A short video about how Integra LifeSciences gets unprecedented visibility with OCI (1:17)
- Oracle Cloud Free Tier to experience OCI
Related stories and resources
Integra adopts OCI for multicloud and gains 90% time savings
In a highly regulated field, Integra LifeSciences turns to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) for improved performance, reduced costs, and superior connectivity.
