Prebuilt machine learning for analytics
Oracle Fusion Analytics provides ready-to-use machine learning (ML) for specific business processes. Additionally, users can leverage the same Fusion Analytics platform services to build their own ML-powered use cases or easily apply self-service ML and predictive analytics with a few clicks, supporting business users, analysts, and data scientists.
Prebuilt machine learning for specific businesses processes
Oracle Fusion Analytics continues to expand its library of ready-to-use machine learning for specific business processes so that users can uncover their own insights and results. Here are some samples:
Predicts risk of a customer paying late or an invoice being paid late. Helps prioritize collections and improve cash flow.
Enables detection and monitoring of adverse impact indicators in hires, terminations, and promotions by gender and ethnicity.
Machine learning platform for data scientists
Oracle Fusion Analytics also includes an enterprise-scale machine learning platform for data scientists to run machine learning within the database, where the data resides. This platform, called Machine Learning in Oracle Database, includes more than thirty ML algorithms to provide no-code automated machine learning. Machine Learning in Oracle Database provides natural interfaces for popular programming languages used in data science, such as SQL, R, and Python.
Most importantly, Fusion Analytics provides citizen data scientists and analysts a self-service method for accessing these models from the central repository and easily executing them on their own datasets to generate predictions.
Self-service ML
Leveraging the capabilities of the underlying Oracle Analytics Cloud, anyone can apply machine learning and predictive analytics to quickly detect anomalies and predict outcomes.
Discover insights with explainable machine learning
The Explain capability enables you to examine any dataset to quickly identify meaningful business drivers and data anomalies with only a few clicks. Get automatic visualizations in return to jump-start new, deeper analyses.

Advanced analytics
Easily apply prebuilt advanced analytics with a few clicks.
- Forecast: Make predictions using prebuilt predictive forecasting models to calculate possibilities for the next set of periods based on past and present data.
- Trend line: Highlight a specific direction in data.
- Clusters: Find groupings of objects showing more of a coherence and proximity to each other than to those in other groups.
- Outliers: Spot outliers and anomalies that are located the furthest away from the average expectations of values.
- Text analytics (e.g. sentiment analysis): Understand the tone, such as negative, positive, or neutral, of responses to surveys or questionnaires.
- Affinity analysis (e.g. market basket analysis): Discover relationships in your data by identifying sets of items that often appear together.
- Graph analytics: Show data relationships visually, such as how people and transactions are connected or the shortest distance between two hubs in a network.
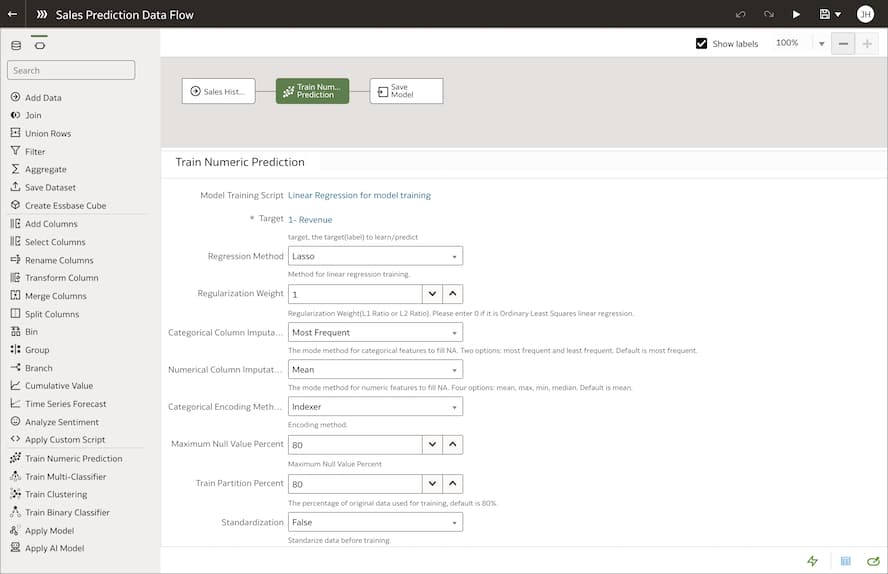
Self-service predictive modelling functions
Oracle Fusion Analytics includes various machine learning algorithms to help build and train predictive models to predict a target value or identify classes of records—no coding required. Examples of available algorithm types include classification and regression trees (CART), logistic regression, and k-means. After the predictive model has been trained, anyone can apply it to any dataset.