 Before You Begin
Before You Begin
This tutorial shows you how to load data from an Oracle Object Store into a database in Autonomous Data Warehouse. This tutorial takes approximately 15 minutes to complete.
Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse Cloud Service Tutorial Series
This is the third in a series of tutorials for Autonomous Data Warehouse. Perform the tutorials sequentially.
- Provisioning Autonomous Data Warehouse Cloud
- Connecting SQL Developer and Creating a Table
- Loading Your Data Into Autonomous Data Warehouse
- Running a Query on Sample Data
- Using Oracle Machine Learning with Autonomous Data Warehouse Cloud (set of additional tutorials)
Background
You can load data into Autonomous Data Warehouse using Oracle Database tools, and Oracle and 3rd party data integration tools. You can load data:
- from files local to your client computer, or
- from files stored in a cloud-based object store
For the fastest data loading experience Oracle recommends uploading the source files to a cloud-based object store, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage, before loading the data into your Autonomous Data Warehouse.
To load data from files in the cloud into your Autonomous Data
Warehouse database, use the new PL/SQL DBMS_CLOUD
package. The DBMS_CLOUD package supports loading
data files from the following Cloud sources: Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure Object Storage, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
Object Storage Classic, and Amazon AWS S3.
This tutorial shows how to load data from Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure Object Storage using two of the procedures in the
DBMS_CLOUD package:
create_credential: Stores the object store credentials in your Autonomous Data Warehouse schema.- You will use this procedure to create object store
credentials in your Autonomous Data Warehouse
adwc_userschema that you defined in a previous tutorial. copy_data: Loads the specified source file to a table. The table must already exist in Autonomous Data Warehouse.- You will use this procedure to load tables in the
adwc_userschema with data from data files staged in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage cloud service. - This tutorial shows how to load data to
SHtables (sales history tables from an Oracle sample schema: SALES, COSTS, TIMES, PRODUCTS, CHANNELS, PROMOTIONS, CUSTOMERS, COUNTRIES, SUPPLEMENTARY_DEMOGRAPHICS). - For more information about loading data, see the documentation Loading Data from Files in the Cloud.
What Do You Need?
- Access to an instance of Autonomous Data Warehouse. See previous tutorials in this series and the documentation: Using Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse Cloud.
- Data files already uploaded to a staging area; otherwise follow the steps in section 1, below, to upload your data files to the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage service.
- To use data files already in an object store, your cloud administrator must provide you the object store credentials and the URL path to the files that you will be copying to your Autonomous Data Warehouse tables.
- If you will be uploading data files to an object store in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage, your cloud administrator must provide you the cloud tenant name, and user name and password with read/write privileges to the object store location where the data is to be stored.
- Oracle SQL Developer (see Oracle
Technology Network download site). Version 18.3 or
later. Versions 18.2 or later contain enhancements for key
Autonomous Transaction Processing features.
Note:
If you are a Windows user on 64-bit platform, download the 'Windows 64-bit with JDK 8 included' distribution as it includes the files necessary to run SQL Developer and connect to your Autonomous Transaction Processing database.
If you are using a SQL Developer version earlier than 18.2, see the documentation topic Connecting with Oracle SQL Developer (earlier than Version 18.2).
 Upload Data Files to Your Object Store
Upload Data Files to Your Object Store
Upload to your cloud-based object store the data files that you want to load to your Autonomous Data Warehouse database. This tutorial uses an object store in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage service.
- Log in to your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console with the following credentials provided by your Oracle Cloud administrator: cloud tenant, user name, password.
- Select Object Storage from the menu at the top left of the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console. Select Object Storage from the sub-menu.
- Select a compartment in which to create a bucket to upload your database table data.
- Click Create Bucket to create the storage bucket in which to upload your source files. You will later copy this staged data into database tables in your Autonomous Data Warehouse.
- Enter a bucket name, select the standard storage tier, and click Create Bucket.
- Click Upload Object to begin selecting the data files to upload to the bucket.
- Navigate to the location of the data files on your local
computer. Drag and drop each file or click Upload
Object to upload each file individually.
This example uploads the data files of theSHtables (sales history tables from an Oracle sample schema). Click here to download a zipfile of the 10SHdata files for you to upload to the object store.
Note: Alternatively, you can usecurlcommands to upload large numbers of files.
- The data files are uploaded to the bucket. These files staged in the cloud are ready to be copied into the tables of your Autonomous Data Warehouse database. Remain logged in to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage.








 Create an Object Store Auth Token
Create an Object Store Auth Token
To load data from an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage object store, you need to create an Auth Token for your object store account. The communication between your Autonomous Data Warehouse database and the object store relies on the Auth Token and username/password authentication.
- If you have logged out of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage, log back in with the following credentials provided by your Oracle Cloud administrator: cloud tenant, user name, password.
- Hover your mouse cursor over the human figure icon at the top right of the console and click User Settings from the drop-down menu.
- Click Auth Tokens under Resources on the left of the console.
- Click Generate Token.
- A pop-up dialog appears. Set the Auth Token by performing the following steps:
- In the pop-up dialog, enter a description.
- Click the Generate Token button.
- Copy the generated token to a text file. The token does not appear again.
- Click Close.





 Create
Object Store Credentials in your Autonomous Data Warehouse
Schema
Create
Object Store Credentials in your Autonomous Data Warehouse
Schema
Now that you have created an object store Auth Token, store in
your Autonomous Data Warehouse adwc_user schema
the credentials of the object store in which your data is
staged.
- Open SQL Developer and connect to your Autonomous Data
Warehouse database as user
adwc_user. See the previous tutorial, Connecting to SQL Developer and Creating Tables, for steps to connect SQL Developer to your Autonomous Data Warehouse database. In that tutorial,WelcomeADWC1!was the suggested password for the useradwc_user. - In a SQL Developer worksheet, use the
create_credentialprocedure of theDBMS_CLOUDpackage to store the object store credentials in youradwc_userschema. - Create a credential name. You reference this credential
name in the
copy_dataprocedure in the next step. - Specify the credentials for your Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure Object Storage service: The username and the
object store Auth Token you generated in the previous step.
begin
DBMS_CLOUD.create_credential (
credential_name => 'OBJ_STORE_CRED',
username => '<your username>',
password => '<your Auth Token>'
) ;
end;
/

After you run this script, your object store's
credentials are stored in your Autonomous Data Warehouse adwc_user
schema.
 Copy
Data from Object Store to Autonomous Data Warehouse Database Tables
Copy
Data from Object Store to Autonomous Data Warehouse Database Tables
The
copy_data procedure of the DBMS_CLOUD
package requires that target tables must already exist in
in your Autonomous Data Warehouse database. In the previous
tutorial, Connecting
SQL Developer and Creating Tables, you created in
your Autonomous Data Warehouse adwc_user schema all
of the target tables.
Now run the copy_data procedure to copy the
data staged in your object store to your Autonomous Data Warehouse adwc_user
tables.
- In a SQL Developer worksheet, use the
copy_dataprocedure of theDBMS_CLOUDpackage to copy the data staged in your object store.- For
credential_name, specify the name of the credential you defined in section 3, Create Object Store Credentials in your Autonomous Data Warehouse Schema. - For
file_uri_list, specify the URL that points to the location of the file staged in your object store. The URL is structured as follows. The values you specify are in bold:
https://swiftobjectstorage.<region name>.oraclecloud.com/v1/<tenant name>/<bucket name>/<file name>
- Click
here for an example script. In the script, use
your own table names, region name, tenant name,
bucket name, and file names.
Note: The region name, tenant name, and bucket name can all be found in one place by clicking the ellipsis option menu and going to file details.
Note: If you receive an error message that youradwc_userdoes not have read/write privileges into the Object Store, you may need to properly set up your user privileges or contact your administrator to do so.
Description of the illustration data_loading_script
- For
- After you run the procedure, observe that the data has
been copied from the object store to the tables in your
Autonomous Data Warehouse database.
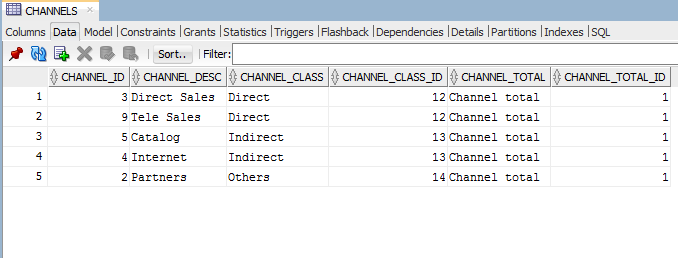
Description of the illustration result_of_loading_table
 Confirm
Your Data Load
Confirm
Your Data Load
All
data load operations done using the PL/SQL package DBMS_CLOUD
are logged in the tables dba_load_operations
and user_load_operations. These tables
contain the following:
dba_load_operations: shows all load operations.user_load_operations: shows the load operations in your schema.
- Query these tables to see information about ongoing and
completed data loads. For example:
SELECT table_name, owner_name, type, status, start_time, update_time,
logfile_table, badfile_table
FROM user_load_operations WHERE type = 'COPY'; - Examine the results. The log and bad files are accessible
as tables:
For more information on monitoring and troubleshooting loads, see the documentation topic Loading Data - Monitoring and Troubleshooting Loads.TABLE_NAME STATUS ROWS_LOADED LOGFILE_TABLE BADFILE_TABLE
---------- ------------ ----------- ------------- -------------
CHANNELS FAILED COPY$1_LOG COPY$1_BAD
CHANNELS COMPLETED 5 COPY$2_LOG COPY$2_BAD
 Next
Tutorial
Next
Tutorial
Running a Query on Sample Data
 Want
to Learn More?
Want
to Learn More?
- Autonomous Data Warehouse website
 Loading
Your Data Into Autonomous Data Warehouse
Loading
Your Data Into Autonomous Data Warehouse