Before You Begin
Purpose
In this tutorial, you learn to perform your first REST API call to Oracle Identity Cloud Service.
Time to Complete
15 minutes.
Background
The REST APIs provide a way to integrate Oracle Identity Cloud Service with custom applications and clients that support REST (such as Java, C#, Go, Python, or Ruby apps), so they can:
- Manage Oracle Identity Cloud Service Users, Groups, Applications, and Settings.
- Perform Federated Single Sign-On (SSO), using OpenID Connect and OAuth 2.0
- Perform Authorization requests with consent, using OAuth 2.0
In this tutorial, you perform your first calls to Oracle Identity Cloud Service using the REST APIs.
Tip: This tutorial serves as a foundation for other REST API tutorials.
What Do You Need?
- Access to Oracle Identity Cloud Service with authorization to manage Applications (Identity Domain Administrator, Security Administrator, or Application Administrator).
- A Linux machine with
cURLutility available.
Tip: For this tutorial, we are using Oracle
Linux 7.2. This tutorial can be executed on other
Operating Systems with bash terminal (such as Red
Hat, Ubuntu, or OSX), or in Windows (using a bash
emulator such as git bash). The commands on
different operating systems may present small
variations.
- It is also recommended that you are familiar with the REST architecture style.
Register a Client Application
In this task, you register an application in Oracle Identity Cloud Service. This step is mandatory for performing REST API requests to Identity Cloud Service. In an application, you can:
- Determine what REST API requests the application will be authorized to perform.
- Obtain credentials (client_id and client_secret) that the application can use to obtain an access token programmatically.
- Obtain the application access token via User Interface to perform REST API calls for testing purposes.
- In the Identity Cloud Service console, expand
the Navigation Drawer
 ,
click Applications, and then click Add.
,
click Applications, and then click Add. - Click Trusted Application or Confidential Application. Tip: The UI provides information about each type of application supported by Oracle Identity Cloud Service.
- Enter the Application Details as follow and click Next.
- In the Client pane, click Configure this application as a Client now.
- Select Client Credentials and JWT Assertion as Allowed Grant Types. Tip: The Allowed Grant Types determine how the application access token can be obtained. The grant types are compliant with the OAuth 2.0 standard.
- On the Client page, scroll
down to the Grant the client access to
Identity Cloud Service Admin APIs.
section, and click Add.
View Image

Description of this image - In the Add App Role dialog
box, select Identity Domain Administrator,
and then click Add.
View Image

Description of this image - Click Next.
- On the following panes, click Next until you reach the last page, and then click Finish.
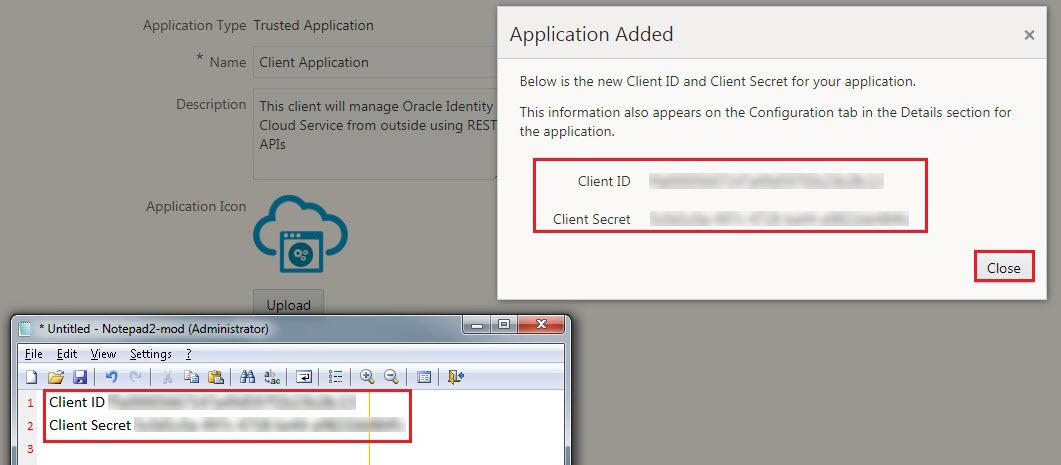
- Copy the Client ID and the Client Secret to a text file, return to the UI, and then click Close.
- Click Activate, and then click Activate Application. A confirmation message appears.
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | Client Application |
| Description | This client will manage Oracle
Identity Cloud Service from outside using
REST APIs |
Get an Access Token
In this task, you obtain an Access Token. The Access Token provides a session (with scope and expiration), that your client application can use to perform tasks in Oracle Identity Cloud Service via REST APIs.
Get an Access Token via REST API
In this task, you learn to obtain an Access
Token via REST API .
For obtaining the token, you will use the client
credentials (client_id and client_secret) obtained
during the application registration.
- In a text editor, prepare the
cURLcommand as follows: - CLIENT_ID: with the Client Application's client id.
- CLIENT_SECRET: with the Client Application's client secret.
- IDCS_URL: with your Oracle
Identity Cloud Service URL (for example,
https://MYTENANT.identity.oraclecloud.com). - Verify the
cURLcommand after replacing the values above and copy its content.curl -k -X POST -u "abcdef1234567899876543210fedcba:98765432-10fe-dcba-0123-456789abcdef -d "grant_type=client_credentials&scope=urn:opc:idm:__myscopes__" "https://MYTENANT.identity.oraclecloud.com/oauth2/v1/token" -o access_token.json - At a command prompt, enter the
cURLcommand. - Open the Access Token file (
access_token.json) in a text editor.
Tip: In this tutorial, we break the result into multiple lines to simplify reading it.
The{ "access_token":"eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJhYmNkZWYxMjM0NTY3ODk5ODc2NTQzMjEwZmVkY2JhIiwidXNlci50ZW5hbnQubmFtZSI6Ik1ZVEVOQU5UIiwic3ViX21hcHBpbmdhdHRyIjoidXNlck5hbWUiLCJpc3MiOiJodHRwczovL2lkZW50aXR5Lm9yYWNsZWNsb3VkLmNvbS8iLCJ0b2tfdHlwZSI6IkFUIiwidXNlcl90ZW5hbnRuYW1lIjoiTVlURU5BTlQiLCJjbGllbnRfaWQiOiJhYmNkZWYxMjM0NTY3ODk5ODc2NTQzMjEwZmVkY2JhIiwiYXVkIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9NWVRFTkFOVC5pZGVudGl0eS5vcmFjbGVjbG91ZC5jb206ODk5MCIsImNsaWVudEFwcFJvbGVzIjpbIkdsb2JhbCBWaWV3ZXIiLCJBdXRoZW50aWNhdGVkIENsaWVudCIsIklkZW50aXR5IERvbWFpbiBBZG1pbmlzdHJhdG9yIl0sInNjb3BlIjoidXJuOm9wYzppZG06dC5vYXV0aCB1cm46b3BjOmlkbTp0Lmdyb3Vwcy5tZW1iZXJzIHVybjpvcGM6aWRtOnQuYXBwIHVybjpvcGM6aWRtOnQuZ3JvdXBzIHVybjpvcGM6aWRtOnQubmFtZWRhcHBhZG1pbiB1cm46b3BjOmlkbTp0LnNlY3VyaXR5LmNsaWVudCB1cm46b3BjOmlkbTp0LnVzZXIuYXV0aGVudGljYXRlIHVybjpvcGM6aWRtOnQuZ3JhbnRzIHVybjpvcGM6aWRtOnQuaW1hZ2VzIHVybjpvcGM6aWRtOnQuYnVsayB1cm46b3BjOmlkbTp0LmJ1bGsudXNlciB1cm46b3BjOmlkbTp0LmpvYi5zZWFyY2ggdXJuOm9wYzppZG06dC5kaWFnbm9zdGljc19yIHVybjpvcGM6aWRtOnQuaWRicmlkZ2UgdXJuOm9wYzppZG06dC5pZGJyaWRnZS51c2VyIHVybjpvcGM6aWRtOnQudXNlci5tZSB1cm46b3BjOmlkbTpnLmFsbF9yIHVybjpvcGM6aWRtOnQudXNlci5zZWN1cml0eSB1cm46b3BjOmlkbTp0LmpvYiB1cm46b3BjOmlkbTp0LnNldHRpbmdzIHVybjpvcGM6aWRtOnQuYXVkaXRfciB1cm46b3BjOmlkbTp0LmpvYi5hcHAgdXJuOm9wYzppZG06dC51c2VycyB1cm46b3BjOmlkbTp0LnJlcG9ydHMgdXJuOm9wYzppZG06dC5qb2IuaWRlbnRpdHkgdXJuOm9wYzppZG06dC5zYW1sIiwiY2xpZW50X3RlbmFudG5hbWUiOiJNWVRFTkFOVCIsImV4cCI6MTQ2MzQ0MjMwOSwiaWF0IjoxNDYzNDM4NzA5LCJjbGllbnRfbmFtZSI6IkNsaWVudCBBcHBsaWNhdGlvbiIsInRlbmFudCI6Ik1ZVEVOQU5UIiwianRpIjoiZGU4NThhMTItNDk2OS00MTgyLTlmODYtZDUyM2U1NTc4NDM3In0.MVu1DNaJr8z236MRE61t2iw2cEvXZwuooqRHTCX9SnM", "token_type":"Bearer", "expires_in":3600 }access_token.json:- Contains the Access Token request output
in JSON format. The return contains the
attributes
access_token,token_type, andexpires_in. - The
access_tokenidentifies your client access in Oracle Identity Cloud Service and will be used for subsequent REST API calls. This token is encoded following the JSON Web Token (JWT) standard.
Tip: To check the JWT token, you can
copy the access_token and verify its value
using: https://jwt.io/#debugger-io
- The
token_typeidentifies the Access Token as a Bearer token type. In future requests, you will use this token type to identify your token in the Authorization header of your request. - The
expires_inidentifies the validity period of the Access Token.
- Contains the Access Token request output
in JSON format. The return contains the
attributes
- Optionally, copy the access_token value and repeat the section Perform Your First REST API Call. You should be able to perform the same calls using the token obtained programmatically.
curl -k -X POST -u "CLIENT_ID:CLIENT_SECRET" -d "grant_type=client_credentials&scope=urn:opc:idm:__myscopes__" "IDCS_URL/oauth2/v1/token" -o access_token.json
Perform Your First REST API Call
In this task, you perform your first a REST API call to Oracle Identity Cloud Service (get a list of Applications). The objective is to show you how the REST API calls are typically executed in Oracle Identity Cloud Service.
Tip: To learn more about the Application API, visit the Oracle Identity Cloud Service REST API documentation.
- In the text editor, prepare the
cURLcommand as follows: - Replace the ACCESS_TOKEN with the access token you copied in the previous task.
- Replace the IDCS_URL with your Oracle
Identity Cloud Service URL. (for example,
https://MYTENANT.identity.oraclecloud.com) - Verify the
cURLcommand after replacing the values above and copy its content. - At a command prompt, enter the
cURLcommand. - Open the
list_of_applications.jsonfile.
Tip: We reduced the command output and broke
it into multiple lines to simplify the reading.
curl -k -X GET -H "Authorization: Bearer ACCESS_TOKEN" "https://MYTENANT.identity.oraclecloud.com/admin/v1/Apps?attributes=displayName" -o list_of_applications.jsoncurl -k -X GET -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJ4NXQjUzI1NiI6Ijg1a3E1MFVBVmNSRDJOUTR6W.eyJzdWIiOiIzOTk3MWY1NTM4N2IzZjhkYWRmZDVhYzIxZjdmNzgzYiIsInVzZXIudGVuYW50Lm5hbWUiOiJGUkVEMSIsInN1Yl9tYXBwaW5nYXR0ciI6InVzZXJOYW1lIiwiaXNzIjoiaHR0cHM6XC.iGqw-btCbixzefAmTDELm4oYgy2qeGA26eBVDeRN-URYiphD_LNUNQHmDsIBColTqkT3MbP5QThmwpLk-sB8tN4nLjTaxyp62pm2V0hw-YLZN4" "https://MYTENANT.identity.oraclecloud.com/admin/v1/Apps?attributes=displayName" -o list_of_applications.json{
"schemas": [ "urn:scim:api:messages:2.0:ListResponse" ],
"totalResults": 1,
"Resources":[ { "displayName":"Client Application", "id":"39971f55387b3f8dadfd5ac21f7f783b" } ],
"startIndex":1,
"itemsPerPage":50
}list_of_applications.json contains
a list of applications that exist in your Oracle
Identity Cloud Service instance.
You've successfully executed your first REST API call.
Want to Learn More?
To learn more about the REST APIs, explore the following tutorials and documents:
- Oracle Identity Cloud Service: REST API documentation
- Oracle Identity Cloud Service: Managing Users via REST APIs
- Oracle Identity Cloud Service: Managing Groups via REST APIs
To learn more about how to use the REST APIs for Federated SSO (using OpenID Connect plus OAuth 2.0), and Authorization scenarios (using OAuth 2.0), explore the following tutorials: