 Before You
Begin
Before You
Begin
In this 15-minute tutorial, you learn how to import a Zeppelin note from a GitHub repository into
Oracle Big Data Manager Notebook. You also learn how to load a comma-separated-value
(.csv) file from the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and an Oracle database table
as new paragraphs into the imported note. Finally, you run the note.
Background
This is the third tutorial in the Integrating GitHub and Oracle Database with Oracle Big Data Manager series. Read them sequentially.
- Registering a GitHub Repository as a Storage Provider with Oracle Big Data Manager
- Registering an Oracle Database as a Storage Provider with Oracle Big Data Manager
- Analyzing Data from Multiple Sources with Oracle Big Data Manager
What Do You Need?
- Access to an instance of Oracle Big Data Cloud Service and the required login credentials.
- Access to Oracle Big Data Manager on an Oracle Big Data Cloud Service instance. A port must be opened to permit access to Oracle Big Data Manager, as described in Enabling Oracle Big Data Manager.
- The required sign in credentials for Oracle Big Data Manager.
- Read/Write privileges to the
/user/demoHDFS directory. - Complete the first two tutorials in this series: The Registering a GitHub Repository as a Storage Provider with Oracle Big Data Manager and the Registering an Oracle Database as a Storage Provider with Oracle Big Data Manager tutorials.
- Access to an Oracle database and the required login credentials.
- Basic familiarity with HDFS, Spark, and optionally, Apache Zeppelin.
 Access the Oracle Big Data Manager Console
Access the Oracle Big Data Manager Console
- Sign in to Oracle Cloud and open your Oracle Big Data Cloud Service console.
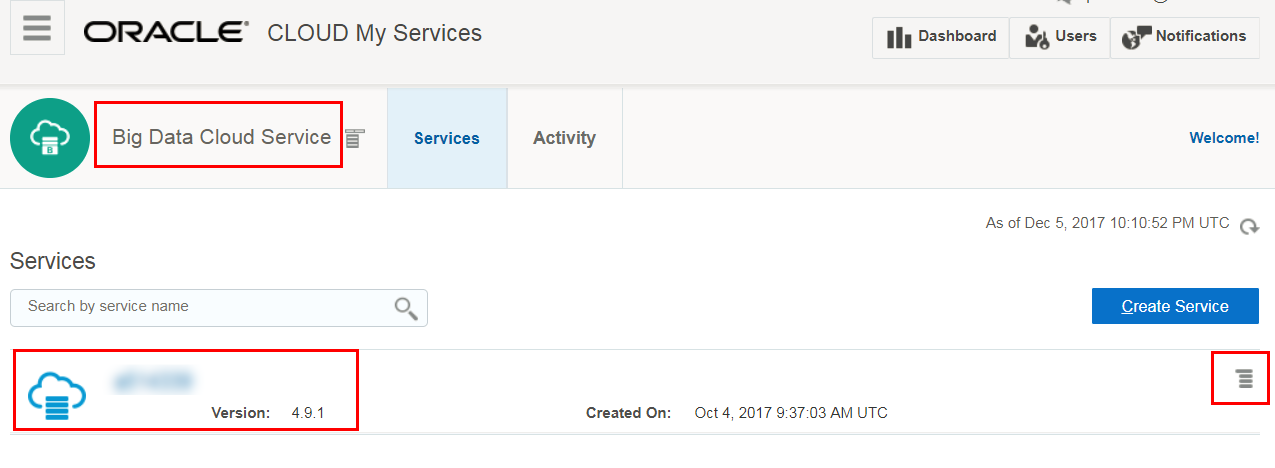
Description of the illustration bdcs-console.png - In the row for the cluster, click Manage this service
 , and then click
Oracle Big Data Manager console from the context menu to display the Oracle Big
Data Manager Home page.
, and then click
Oracle Big Data Manager console from the context menu to display the Oracle Big
Data Manager Home page.
 Import a Zeppelin Note from GitHub into Oracle Big Data
Manager Notebook
Import a Zeppelin Note from GitHub into Oracle Big Data
Manager Notebook
In this section, you import a Zeppelin note from a GitHub repository into Oracle Big Data Manager Notebook.
- On the Oracle Big Data Manager page, click the Data tab.
- In the Data explorer section, select Github (github)
from the Storage drop-down list. The
bdm-notebook-demoGitHub repository that you registered in the first tutorial is displayed in the Name column. Double-click the repository name and navigate to themasterbranch. This branch contains theNotebook.jsonZeppelin note that you will import into Oracle Big Data Manager Notebook.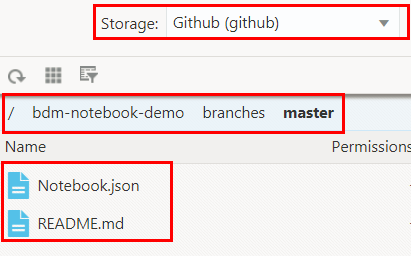
Description of the illustration master-branch.png - Right-click the
Notebook.jsonfile. From the context menu, select Notebook, and then Import as Notebook Note. The Import as Notebook Note dialog box is displayed. - Enter
HDFS and Oracle Database Data Analysisin the Note name field, and then click Create. TheHDFS and Oracle Database Data Analysisnote is imported and displayed in Notebook. The initial status of each paragraph in the note isREADYwhich indicates that the paragraph has not been executed yet.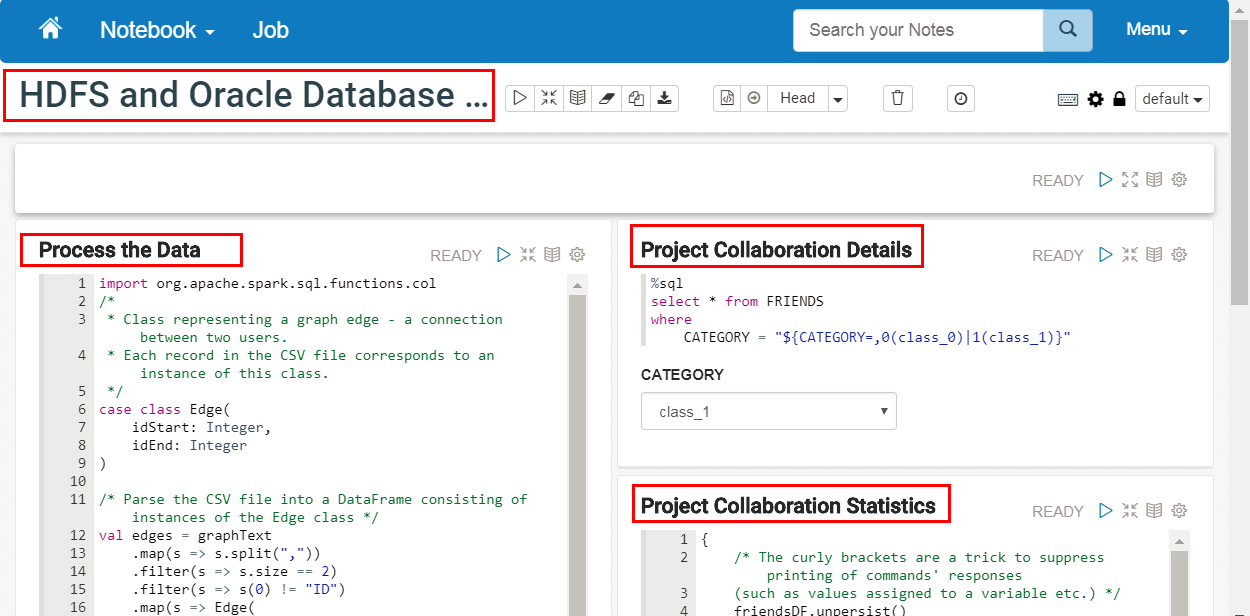
Description of the illustration display-note.png - The empty paragraph at the top of the note uses the
%mdMarkdown interpreter to generate static html from Markdown plain text. Click Run this paragraph(Shift+Enter) on the paragraph's toolbar to display
detailed information about this note.
on the paragraph's toolbar to display
detailed information about this note.
 Import Oracle JDBC Driver to Oracle Big Data Manager
Notebook
Import Oracle JDBC Driver to Oracle Big Data Manager
Notebook
In this section, you add the Oracle JDBC driver to the Spark interpreter classpath in Oracle Big Data Manager. This enables Spark to connect to the Oracle database.
- On the Oracle Big Data Manager page, click the Notebook tab.
- Click the Menu drop-down list, and then select Interpreter. The Interpreters page is displayed.
- Scroll-down to the spark interpreter section, and then click edit.
- Scroll-down to the Dependencies section, enter the following path to the Oracle JDBC driver in the artifact field to allow the Spark interpreter to create a DataFrame that connects to the Oracle database, and then click Save.

/usr/lib/oracle/12.1/client64/lib/ojdbc7.jar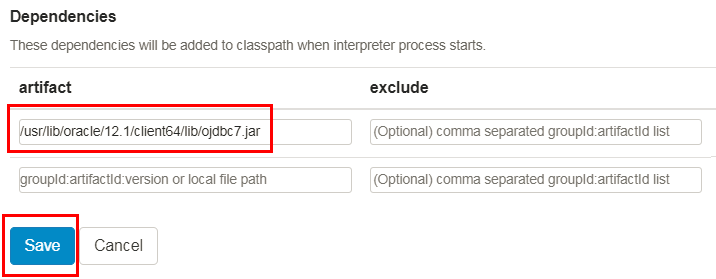
A Do you want to update this interpreter and restart with new settings? confirmation message is displayed. Click OK.
 Load an HDFS File as a Paragraph into the
Imported Note
Load an HDFS File as a Paragraph into the
Imported Note
In this section, you upload the edges.csv file to HDFS and load the file as a new
paragraph into the imported note. The edges.csv file contains two columns. Each column represents a student id. The
two student ids in each row represent two students who are collaborating on a specific class project.
- Right-click the edges.csv file, select Save link as... from the context menu, and then save it to your local machine.
- Upload the
edges.csvfile to HDFS. On the Oracle Big Data Manager page, click the Data tab. In the Data explorer section, select HDFS storage (hdfs) from the Storage drop-down list. Navigate to the/user/demodirectory, and then click File upload on the toolbar.
on the toolbar.
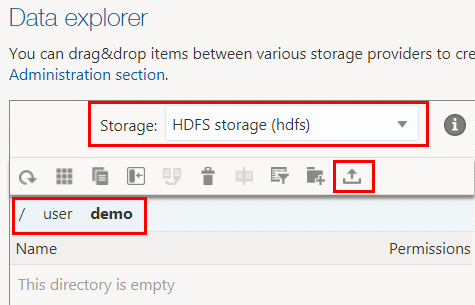
Description of the illustration file-upload.png - In the Files upload dialog box, click Choose files
to upload. In the Open dialog box, navigate to your local directory
that contains the
edges.csvfile, and then select the file. Theedges.csvfile is displayed in the Name column. Click Upload. - Drill-down on the Details section in the Files upload
dialog box to display the progress of the file upload operation. When the file is uploaded
successfully to HDFS, the Upload has finished message is displayed. Click
Close to close the dialog box. The
edges.csvfile is now displayed in the/user/demoHDFS directory. - Right-click the
edges.csvfile. From the context menu, select Notebook, and then Load as general file. The Load file in Notebook wizard is displayed. It has three pages: Paragraph settings, Note settings, and Overview. - In the Paragraph settings wizard page, enter
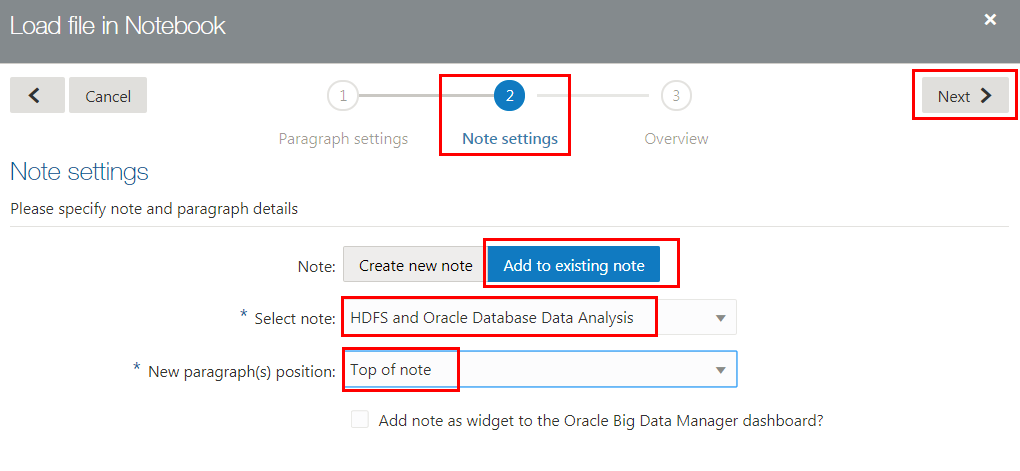
Load Data from HDFSin the Paragraph name field. Selectsparkfrom the Interpreter drop-down list, and then click Next. - In the Note settings wizard page, select Add to existing note
in the Note field. Select the
HDFS and Oracle Database Data Analysisnote from the Select note drop-down list. Select Top of note from the New paragraph(s) position drop-down list, and then click Next. - In the Overview wizard page, review the settings. If you need to make a
correction, click the back arrow
 . If you are satisfied with the settings, click Finish to display the updated note. The new Load Data from HDFS paragraph is displayed at the top of the updated
note.
. If you are satisfied with the settings, click Finish to display the updated note. The new Load Data from HDFS paragraph is displayed at the top of the updated
note.
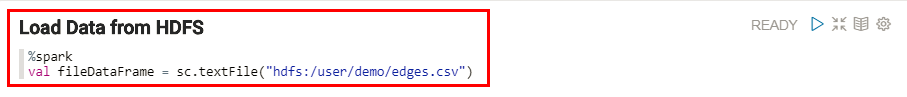
- The new Load Data from HDFS paragraph uses the
%sparkSpark interpreter to create a DataFrame that references theedges.csvfile that you uploaded earlier to the/user/demoHDFS directory. This DataFrame is stored in thefileDataFramevariable. Rename this variable tographText.The Process the Data paragraph in this note references thegraphTextvariable.val graphText = sc.textFile("hdfs:/user/demo/edges.csv")
 Load an Oracle Database Table into the Imported Note
Load an Oracle Database Table into the Imported Note
In this section, you load the USERS Oracle database table that you created in the
second tutorial as a new paragraph into the imported note. The USERS table contains
information about each student's name, id, and class category.
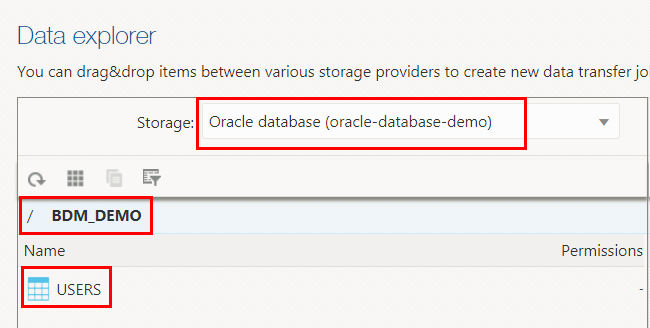
- On the Oracle Big Data Manager page, click the Data tab. In the Data
explorer section, select
Oracle database (oracle-database-demo)from the Storage drop-down list. Navigate to your schema that contains theUSERStable that you created earlier. In this example, we created theUSERStable in the BDM_DEMO schema. The table is displayed in the Name column. - Right-click the
USERStable. From the context menu, select Notebook, and then Load table. The Load table in Notebook wizard is displayed. It has three pages: Paragraph settings, Note settings, and Overview. - In the Paragraph settings wizard page, enter
Load Data from Oracle Database Tablein the Paragraph name field. Selectsparkfrom the Interpreter drop-down list, and then click Next. - In the Note settings wizard page, select Add to existing note
in the Note field. Select the
HDFS and Oracle Database Data Analysisnote from the Select note drop-down list. Select Top of note from the New paragraph(s) position drop-down list, and then click Next. - In the Overview wizard page, review the settings. If you need to make a
correction, click the back arrow
 . If you are
satisfied with the settings, click Finish to display updated note.
Two new paragraphs are added at the top of the note.
. If you are
satisfied with the settings, click Finish to display updated note.
Two new paragraphs are added at the top of the note. - Click the title of the top new paragraph. The title becomes active in read/write mode. Rename the title to
Load Data from Oracle Database Table.Rename the title of the second new paragraph toCount Number of Students.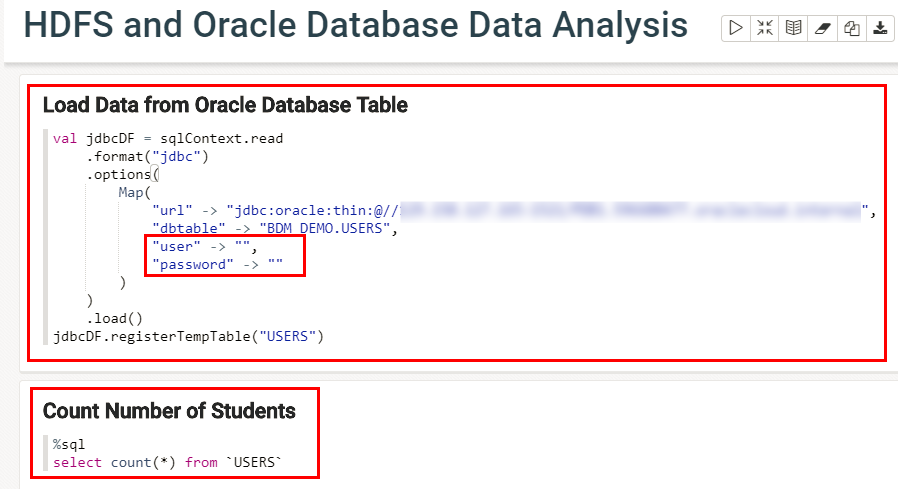
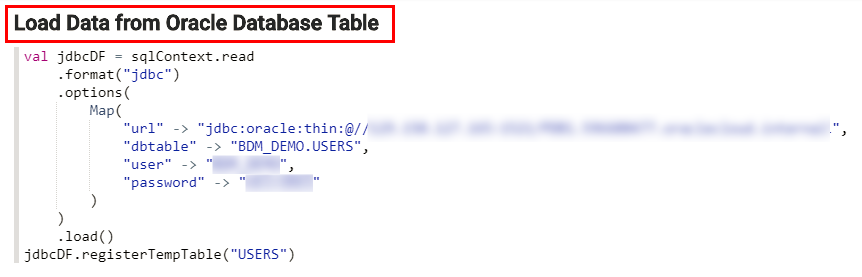
Description of the illustration oracle-database-paragraphs.png When you load a relational database table into a note, Oracle Big Data Manager creates two paragraphs. The first paragraph creates the
jdbcDFDataFrame which references theUSERStable in your Oracle database. It also registers thejdbcDFDataFrame as a temporary table namedUSERS.You can run SQL queries on this temporary table. The second paragraph uses the%sqlinterpreter which enables you to execute a Spark SQL query. This simple query counts the number of rows in theUSERStable. - Make sure that the url field references your host name and port # where your Oracle database is running. Enter your Oracle database username in the empty user field. Enter your Oracle database password in the empty password field.
 Run the Note
Run the Note
In this section, you run the updated note and review the output.
- Click Run all paragraphs
 on the Note's toolbar to run all paragraphs in this note. A Run all paragraphs
confirmation message is displayed. Click OK. When a paragraph executes
successfully, its status changes to
on the Note's toolbar to run all paragraphs in this note. A Run all paragraphs
confirmation message is displayed. Click OK. When a paragraph executes
successfully, its status changes to FINSIHED. - The output of the Count Number of Students paragraph is displayed in the default table format in the result section at the bottom of the paragraph.
- The Process the Data paragraph performs most of the analysis on the dataset.
It joins the HDFS data with the Oracle database table data. The code accesses the two
idcolumns from theedges.csvfile, and then uses theUSERStable as a look-up table to find the associated names and class categories for those student ids. The code then registers the joined data as a new temporary table namedFRIENDS. This new table contains six columns which represent the two students collaborating on a project from theedges.csvfile. Finally, the code counts the number total projects, same-class projects, and cross-class projects. These values are used and displayed in the Project Collaboration Statistics paragraph.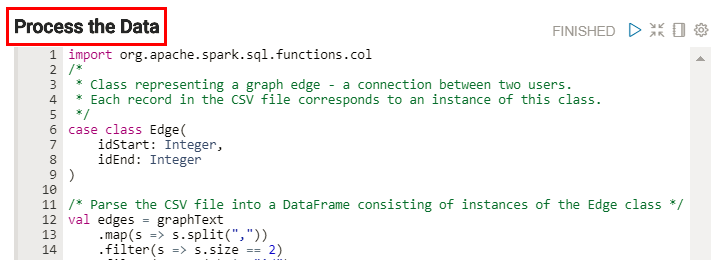
Description of the illustration process-data-paragraph.png - The output of the Projects Collaboration Details paragraph is displayed in the default table format in the result section at the bottom of the paragraph. The following image shows the partial output.
- The output of the Projects Collaboration Statistics paragraph is displayed in the result section at the bottom of the paragraph.
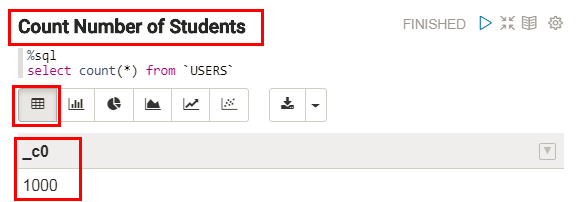
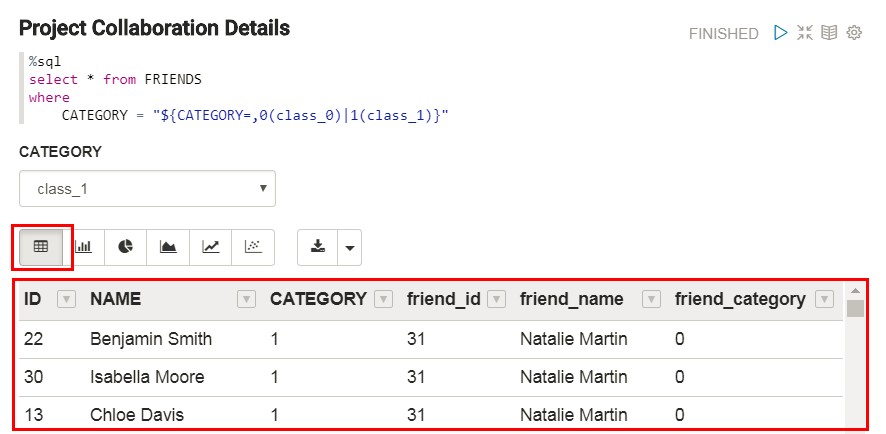
Note: The results of the SQL query are returned in an arbitrary
order unless you use the order by clause followed by the column(s) name; therefore, your results might not match the result shown in the image.
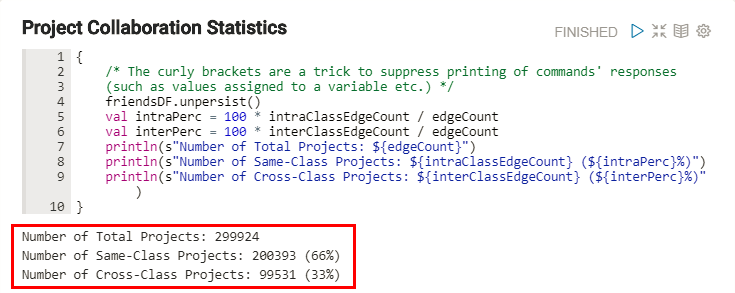
 Analyzing Data from Multiple Sources with Oracle Big Data Manager
Analyzing Data from Multiple Sources with Oracle Big Data Manager